Date
In undb, the Date type field is designed to store and manage date-related data. This field type is essential for tracking events, scheduling, and organizing data based on time-sensitive information.
Key Features of Date Type
1. Date Storage
- Date Values: The Date field is used to store calendar dates. This can include dates for events, deadlines, creation dates, or any other type of time-based data.
2. Display Format
- Customizable Formats: Dates can be displayed in various formats (e.g., YYYY-MM-DD, MM/DD/YYYY, DD/MM/YYYY) depending on your preferences or regional standards. This ensures that the data is presented in a way that is most intuitive for your users.
- Time Inclusion Option: You can choose whether to include time along with the date. When time is included, a time picker will be available for precise time selection.
3. Constraints
Date fields in undb can include several constraints to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the data:
- Required: You can specify whether the Date field is mandatory. If set as required, every record must include a valid date before it can be saved.
- Minimum Date: Set a minimum allowable date to ensure that dates entered are not earlier than a specific threshold (e.g., no dates before the year 2000).
- Maximum Date: Similarly, you can set a maximum date to prevent future dates beyond a certain point, which is useful for planning or historical data.
4. Default Value
- Setting a Default Date: You can define a default date for the field using either:
- A specific fixed date
- Date macros (e.g.,
@nowfor current date/time) - No default value
5. Date Macros
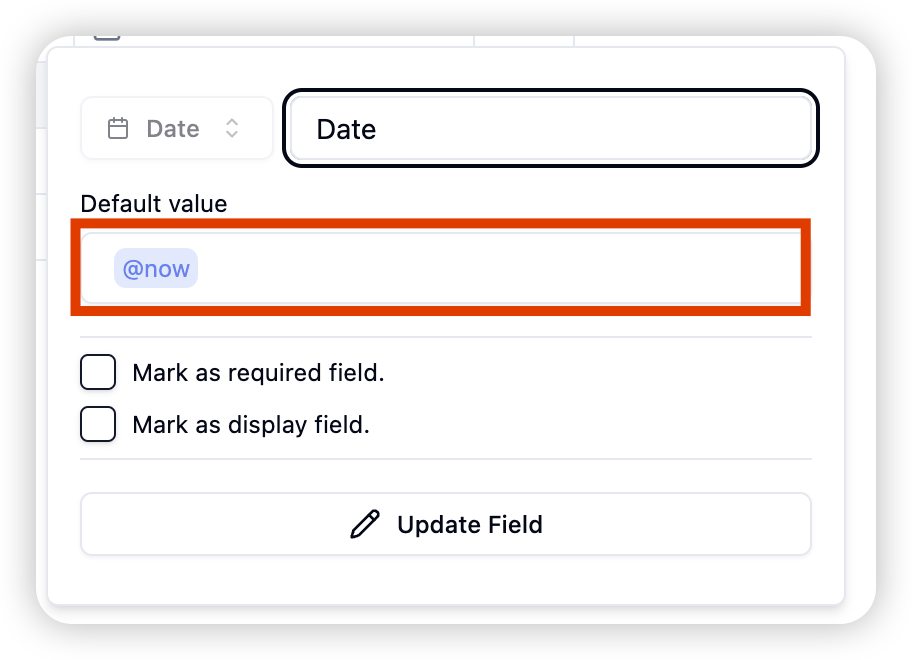
The Date field supports several built-in macros for dynamic date values:
- @now: Sets the field to the current date and time
- @today: Sets the field to the current date (start of day)
- @tomorrow: Sets the field to tomorrow’s date
- @yesterday: Sets the field to yesterday’s date
These macros are particularly useful when setting default values or creating new records that need to reference the current time or relative dates.
6. Use Cases
- Event Scheduling: Use the Date field to track when events are scheduled to occur, such as meetings, appointments, or project milestones.
- Historical Records: Store creation dates, modification dates, or any other significant historical data points.
- Deadlines and Due Dates: Manage deadlines by setting dates for tasks, assignments, or other time-sensitive activities.
By utilizing the Date type field in undb, you can effectively manage time-based data, ensuring that all your records are accurately tracked and easily accessible based on their date attributes.